The Internet of Things (IoT) is one of the most popular current technologies and around ten thousand startups are present in this sector.
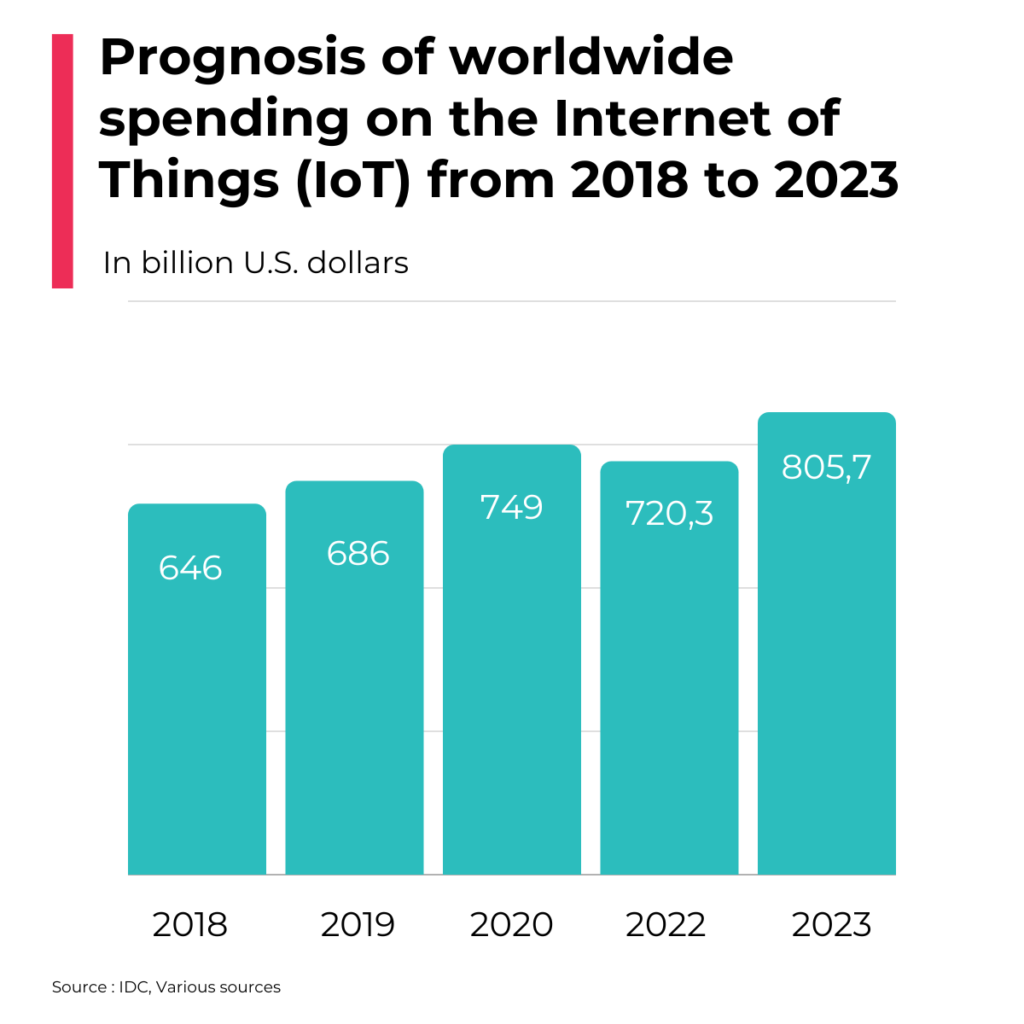
Some countries have understood very fast that IoT is the technology that will change the world. The investments are significant and the adoption rates for IoT are stimulated by governments’ policies, subsidies and research projects. In 2023, 805 billion U.S. dollars were spent on the Internet of Things (IoT) technology worldwide. Statista’s research found countries that are expected to spend the most by 2023 on the IoT market are the U.S. with 172 billion USD, followed by China with 147 billion USD, Japan 32 billion USD and Germany 30 billion USD. Amazingly, India ranked fifth at 27 billion USD, overtaking European countries such as France (22 billion USD) and the U.K. (26 billion USD).
When it comes to IoT changing the world, one of the main points of IoT are the sensors. These devices are responsible for collecting data from outside and communicating them over the Internet.
In the health sector, these sensors, placed directly on humans’ bodies, collect information and send it directly to software for analyzing their well-being. The vehicles thanks to these sensors are a powerful communication device and autonomous vehicles are already proving their efficiencies. We know that equipped with sensors, they will communicate with each other and with different elements on the road to achieve smoother and safer traffic. For the industry 4.0 the IoT sensors and technologies are powering them like a nervous system which multiplies the productivity significantly. As well, IoT appears, again, in the center of concepts such as smart city. Cities will be connected at more levels than we can even expect. IoT will also enter our homes and lives through all kinds of devices that will seek to make our lives a little more comfortable.
We are all watching with amazement the change taking place with an unexpected speed whether we like it or not. Maintaining the security and privacy of citizens are issues which are already the subject of concern. With current IoT technologies, these concerns will increase their importance in the future. Perhaps the concern about the security and privacy in European and North American countries are more and more influencing the speed of adoption and of decisions on investment in these technologies and that is allowing the Asian countries to take the lead over this market?
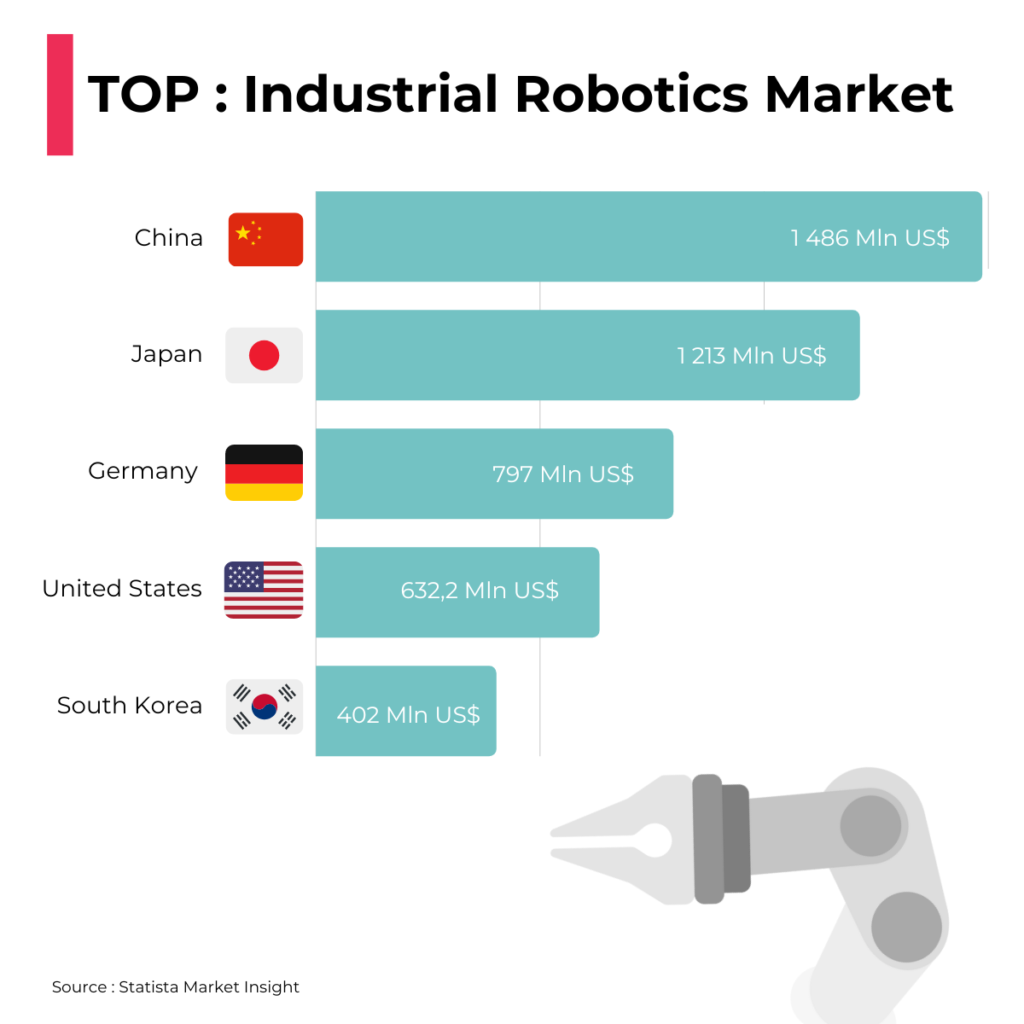
50% of the global robot sales in five countries. Same trend for IoT?
There are five major markets representing 50% of the total industrial robotics sales in 2023: China, Japan, Germany, the United States and the Republic of Korea. Since 2016 China has been the biggest robot market in the world with a continued dynamic growth.
According to a recent McKinsey study, the most impacted sector by the IoT by 2025 will be industrial manufacturing. Another study by IFR, showed that in terms of demand for industrial robots in 2020, robot sales slightly increased to 384,000 units. It is expected that in 2024, global industrial robot shipments will amount to about 518,000. The electronics industry surpassed the automotive industry in terms of annual robot installations in 2020 and held on to this position in 2021, installing 26% of all robots installed that year. The automotive industry followed with 23% of installations mainly driven by the parts supplier segment.
According to IFR, robot installations in Europe are expected to grow slowly. The war in Ukraine and the trade embargo on Russia, the threat of cutting natural gas supplies, and the tightening of monetary policies are weakening the propensity to invest.
Are IoT patent applications a predictor of future world leadership for China and Asia?
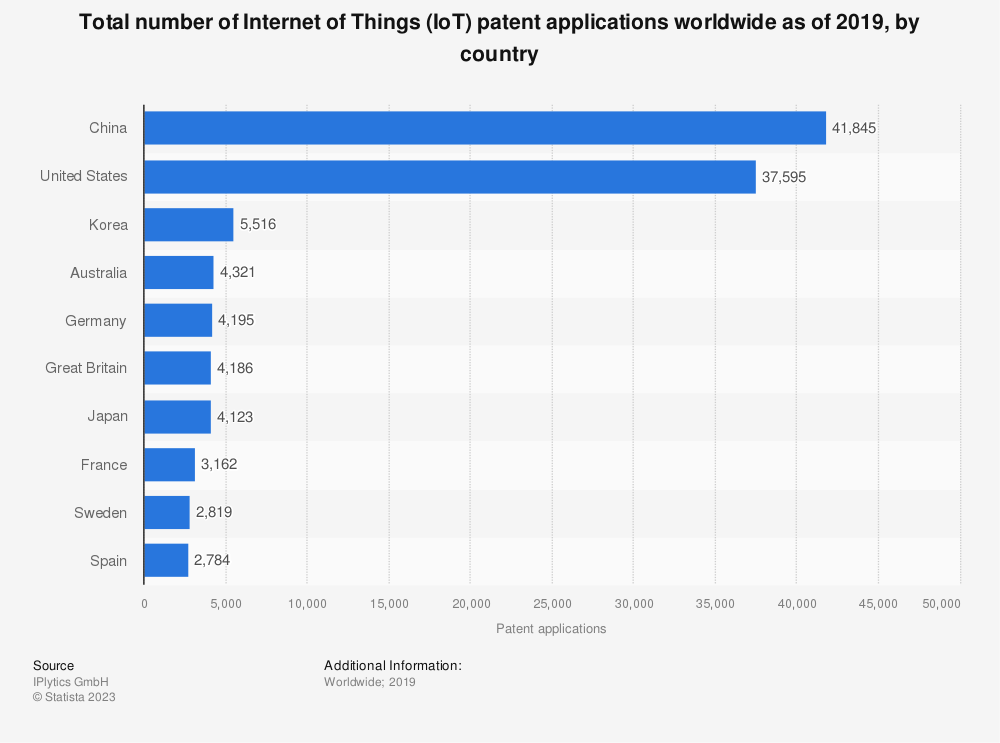
According to research conducted by IPlytics, 41 845 IoT patent applications have been filed in China to date, making it the world’s largest processor of IoT patent applications followed closely only by USA with 37 595 applications. Asia is the region claiming the leadership in IoT. The representation above shows that Korea, Australia and Japan are overtaking countries such as Germany, Great Britain and France. South America and Africa are two regions lagging behind in the IoT patent applications.
The stakes are high for new players entering the IoT country game and to be able to succeed, smart and specific industries focused strategies might be the key.
Consumer IoT
Internet of Things for consumer applications, has seen tremendous growth in recent years as more and more devices are being connected to the internet. From smart thermostats to connected doorbells, consumers are embracing the convenience and control that these devices offer.
According to Statista, revenue in the consumer IoT market is projected to reach US$183bn in 2023. Revenue is expected to show an annual growth rate (CAGR 2023-2028) of 4.83%, resulting in a market volume of US$232bn by 2028. In global comparison, most revenue will be generated in the United States (US$24bn in 2023).
One of the biggest challenges is ensuring the security and privacy of consumer data. As more and more devices are connected to the internet, there is a growing risk of cyberattacks and data breaches. Companies must invest in robust security measures and protocols to protect consumer data and prevent unauthorized access.
According to the Cyber Threat Report 2023 by SonicWall, the number of Internet of Things (IoT) attacks in the world reached over 10.54 million in December 2022. However, in the same month of 2021, the number of reported IoT attacks dropped to nearly six million. The highest number of monthly attacks was detected in June 2022, with approximately 13 million attacks.
Smart Home
The Smart Home devices are networked devices and related services that enable home automation. Considered are devices that are connected directly or indirectly via a so-called gateway to the Internet. Their main purposes are the control, monitoring and regulation of functions in a private household. A part of the internet of things, smart home systems and devices often operate together, sharing consumer usage data among themselves and automating actions based on the homeowners’ preferences.
Revenue in the Smart Home market is projected to reach US$118bn in 2022 and is expected to show an annual growth rate (CAGR 2022-2027) of 12.47%, resulting in a projected market volume of US$223bn by 2027. Household penetration will be 14.2% in 2022 and is expected to hit 28.8% by 2027. A global comparison reveals that most revenue is generated in the United States, China, the United Kingdom, Japan and Germany.
Thus far, the Smart Home market has been faced with challenges in terms of compatibility between devices. The presence of different ecosystems, diverse communication protocols, and the absence of a universal standard have restricted consumer choices and often led to complications during setup. When we purchase a smart home device, bring it home, and connect it, our expectation is for it to function seamlessly without any additional setup, particularly in terms of linking with other devices on our local network. Given this scenario, the emergence of the new universal standard, known as “CHIP” Short for “Connected Home over IP,” it’s a work group that plans to develop and promote the adoption of a new, royalty-free connectivity standard to increase compatibility among smart home products. The project is supported by a coalition of 200 companies including Amazon, Apple, Google, and Samsung, representing a promising development for Smart Home technologies. It has the potential to facilitate communication among all devices adhering to this standard, regardless of their manufacturer.
Company perspective
The global expansion of 5G networks will have a profound impact on the capabilities of smart home devices, giving opportunities to IoT companies. 5G, representing the fifth generation of wireless technology, is anticipated to deliver speeds ranging from ten to fifty times faster than current 4G networks. According to Statista there are major disparities between countries. For example, in Japan and Italy, the average minimum performance of 5G is currently only one-and-a-half times higher than 4G, while speeds have increased six- and seven-fold in the UK and Australia respectively. South Korea, the first country to launch 5G in December 2018, provides a glimpse of the technology’s true potential. By the first half of 2021, Korean users could expect download speeds at least twelve times faster than 4G. This advancement enables a more extensive exchange of data among smart home devices with other data-intensive applications such as 3D gaming, augmented reality, virtual reality, smart city technologies, and autonomous vehicles.




